** The Old Nordic name for the world we occupy.
Klevius wrote:
Saturday, June 20, 2015
Klevius Midsummer quiz: How come that Klevius can read Beowulf but modern Brits can not?!
Klevius question to BBC: Why so much focus on Muhammad and so little on Beowulf?
The simple answer is that as a Finland-Swede Klevius happens to master not only Swedish and Finnish but also old Finland-Swedish dialects - and in an extension most old wordings based on Old Nordic (aka Old Norse) over an area covering all the Nordic countries (incl. Gotland) plus Netherlands, England, Scotland plus most of the north Atlantic islands east of Iceland.
In the 1990s when Klevius studied English at Stockholm University they offered a video recording of a play based on thousand year old English texts. To Klevius astonishment he immediately recognized many familiarities with the East-Nyland dialects Klevius had grown up with. So when two Norwegian linguists a couple of years ago stated that English is a Scandinavian language Klevius applauded them.
So what does this have to do with Midsummer? Well, it's not just linguistics but a load of other familiarities as well, not to mention the fire feasts which may even be traced back to the Celts. And remember that much/most pre-Christian cultural influences are shared within all the Nordic countries.
For a background take a look at Kvenland:
Klevius wrote
Thursday, August 07, 2014
Who were the most evil ones, muslims or Vikings?
While Yazidi people (the original monotheists from which Jews, Christians and muslims took their "faiths") and other non-muslims (and wrong-muslims) are raped, terrorized, slaughtered or forced to "convert" to islam, Ahmed and Warsi are busy defending the muslim terror organization Hamas
Take a look at the two faces in the middle of this pic that Klevius has used for many years to enlighten the problem with islam. They are both old pals fighting for political islam and against Human Rights - not necessarily for the parties they repesent. Ahmed is a muslim who uses Labor party in his jihad while Warsi uses the Conservative party in hers. They are both rooted in Pakistan (Kashmir area) and they have both been deeply involved in scandals that would have put a non-muslim far away from any political post. More about Warsi furthest down on this posting.
A glossy popular history magazine now describes plundering Medieval muslims and Vikings in completely opposite ways. Why?!
Whereas 'the caravan robbing muslims' (and that's what the magazine actually writes) are called 'the followers of a new faith' and their plundering in Mideast, Africa, Asia and Europe is positively described as 'successful conquest' (while the European defense is called 'evil crusaders'), the Vikings are just negatively dismissed as evil 'Barbarians' from the north who 'devastated the whole of Europe'.
Klevius history lesson about the muslims and the Vikings
The "extremist" parts of the Koran are exactly the ones that count for true muslims and historical records. Without following precisely those extremist parts of the Koran there wouldn't have been any islam at all.
However, although the Viking phenomenon as such was a direct consequence of muslim evilness, the forceful Vikings themselves didn't come out of the blue but represented an amplification of a pre-existing historical pattern that goes back to the Goths. And so far only Klevius (who is a late Goth/Finland-Swede) seems to have found the quite obvious source code for this transition.
In short it goes as follows:
This advanced sword from Vendel in Uppland Sweden is dated to a time before the Vikings when Uppland was still generally Finnish or at least bi-lingual. It's just one of many examples clearly revealing an alternative understanding of how the "barbarian" "Pagans" from the north could topple the Christian Roman empire. Although the sword is from Vendel time, i.e. after the fall of the Romans, it has to be put in context with the Goths (see below).
Birka (east of Stockholm) was established in the middle of the 8th century and thus being one of the earliest urban settlements in Scandinavia. Birka became part of a Baltic/Bay of Finland link in the pre-existing river and portage routes through Ladoga (Aldeigja) and Novgorod (Holmsgard) to the Byzantine Empire and the parasitic islamofascist Abbasid slave Caliphate.
The Goths
Acknowledgement: It's extremely problematic and even embarrassing for Klevius as a Finland-Swede, and as a person who brags about self-criticism being his main scientific tool, to end up with his own ethnicity as having been a major global player in the past. However, there are some mitigating excuses. So for example, what made some Finland-Swedes to become Goths and Vikings etc. were not necessarily the most sought after human characteristics. Moreover, those Finland-Swedes who didn't participate became today's tiny and on the verge of extinction Finland-Swedish community, linguistically bullied by the Finns (language) as well as the Swedes (accent/dialects).
Btw, dear reader, why don't you dare to comment, ask questions etc? Isn't the topic interesting and challenging enough, or is it because you're a coward and don't want to be known as reading something critical of islam, the worst ideological crime ever against humanity?
The oldest runic inscription found is some 600 years before the Viking age - and it is Finnish (or more probably Finnish-Old Nordic, i.e. what Klevius terms Finland-Swedish)
This is the oldest runic (Futark) inscription found. It says HARJA which is exactly the same as 'harja', meaning comb or , brush or ridge, in modern Finnish. The word is etymologically very old and had this Finnish form when the comb was made, i.e. it cannot be confused with some non-Finnish interpretation. Moreover, the word is found in all sister languages. The possibly related Baltic (or other) words do not resemble it at all neither now nor back then. The comb was found in Denmark and is dated to 160 CE (same time as the birth of Fornjotr, king of Kvenland and Gotland). However, also keep in mind that the combs owner also spole old Nordic.
Warning! There are many confused "scientists" out there emotionally trying to dismiss the Nordic origin of the Goths. I even stumbled on one who thought that different spellings would mean different groups. Spellings etc don't matter here. Just like 'Vikings' the 'Goths' is more of a concept than a specific ethnicity - just like 'muslims', except for the fact that muslim evilness is still kept alive under the cover of 'religion'.
The name 'Goth' (in its many variants) reflects the fact that it's not only thoroughly anchored in a Finnish-Old Nordic geographical/linguistic area and context but also that Gothic is linguistically puzzling if you don't see it as an Uralic colored form of Old Nordic. Moreover, genetics is still in its cradle and hence an extremely fragile tool. Only very crude main chronologies can so far be established and even shallow dives result in progressive guesswork at best, no matter how fancy math and graphs are produced. Klevius will explain more on this exciting topic later. However, so far nothing in genetics seems to disprove Klevius' analysis.
To understand the confusing picture about Finnish-Old Nordic relations that seems to emerge, one has to consider the relation between Indoeuropean and Uralic/Finnish languages. Both groups stem from geographically overlapping areas. However, whereas the former was more sedentary and farming oriented the latter was older and more rooted in a hunter-gatherer context.
As we all know agricultural societies usually gained more wealth and population than nomads etc. So when they moved north the Germanic tribes tended to follow a path more favorable for farming (Germany, Denmark and southern Sweden). This is how the linguistic map evolved in northern Europe, divided between the Finnish/Uralic related and Germanic/Indoeuropean tribes.
The Langobards - an example of how a tiny amount of Finland-Swedes (Kvens) conquered Europa
The Lombards or Langobards (Germanic word meaning the 'long-bearded' or the 'long-boarded') Latin: Langobardī, Italian Longobardi), were a north Germanic (Gothic?) tribe traceable to Gotland (Scadanan) who ruled Italy from 568 to 774.
Paul the Deacon wrote in the Historia Langobardorum that the Lombards descended from a small tribe called the Winnili (or Vinnili or Finnili) who dwelt in southern Scandinavia (Scadanan, i.e. Gotland) before migrating to seek new lands. In the 1st century AD they formed part of the Suebi*, in northwestern Germany. By the end of the 5th century they had moved into the area roughly coinciding with modern Austria north of the Danube river, where they subdued the Heruls and later fought frequent wars with the Gepids. The Lombard king Audoin defeated the Gepid leader Thurisind in 551 or 552; his successor Alboin eventually destroyed the Gepids at the Battle of Asfeld in 567.
* From Proto-Germanic *swēbaz, either based on the Proto-Germanic root *swē- meaning "one's own" people, or on the third-person reflexive pronoun; or from an earlier Indo-European root *swe-. The etymological sources list the following ethnic names as also from the same root: Suiones, Semnones, Samnites, Sabelli, Sabini, indicating the possibility of a prior Indo-European ethnic name, "our own people". Ultimately the word may also be related to 'sib' with similar meaning.
Following this victory, Alboin decided to lead his people to Italy, which had become severely depopulated after the long Gothic War (535–554) between the Byzantine Empire and the Ostrogothic Kingdom there. The Lombards were joined by numerous Saxons, Heruls, Gepids, Bulgars, Thuringians, and Ostrogoths, and their invasion of Italy was almost unopposed. By late 569 they had conquered all the principal cities north of the Po River except Pavia, which fell in 572. At the same time, they occupied areas in central and southern Italy. They established a Lombard Kingdom in Italy, later named Regnum Italicum ("Kingdom of Italy"), which reached its zenith under the 8th-century ruler Liutprand. In 774, the Kingdom was conquered by the Frankish King Charlemagne and integrated into his Empire.
Vikings
From Altai to Gotland, Sami, God, Vikings, Shakespeare and Tolkien
Klevius etymology and history remarks relating to the Britain-Scandinavia connection: The ancient Persian (which is extremely young compared to Uralic) word for god 'khoda' connects to the even more ancient Finnish 'koti' and Finno-Ugric 'kota' (=home/house/seed vessel - see Klevius definition of religion and the Vagina gate), Saami 'goahti'. German Gott (god) and Swedish gott (good) as well as Gotland (pronounced Gottland), the island in the Baltic sea that constituted a (the?) main Viking hub in their slave trade with Jews and muslims.
Gotland in particular is famous as the probable ancestral home of the Goths: "a Gothic population had crossed the Baltic Sea before the 2nd century AD, reaching Scythia at the coast of the Black Sea in modern Ukraine where Goths left their archaeological traces in the Chernyakhov culture. In the 5th and 6th centuries, they became divided as the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, and established powerful successor-states of the Roman Empire in the Iberian peninsula and Italy. Crimean Gothic communities appear to have survived intact in Crimea until the late 18th century.
The father of Shakespeare's prototype for Hamlet was a Goth from the Gothenburg area in Sweden (were Klevius father also happened to be born). These Goths came originally from Gotland via those very same waterways that were shaped already some 9,000 years ago, hence connecting the Baltic Sea with Doggerland/North Sea.
Gotland was also the home port and treasure island for the Vikings because it naturally connected West and East via Staraja Ladoga southeast of Finland on the river way down to the south. Gotland has revealed the biggest hoards of Viking age old Arab/islamic silver coins in Northern Europe.
Immediately north of Staraja Ladoga is the homeland of the Finnish national epic Kalevala which Tolkien based his writing on.
The world's oldest fishing net is found in southeastern Finland and is some thousand years older than Cheddar man the "oldest Brit".
Bromme culture existed in what is today's Sweden already 11,700–11,000 bp.
As a curiosity it might be noted that film director Ingmar Bergman lived most of his life on Gotland where some of his most powerful movies were filmed.
In conclusion one might well argue that the Baltic Sea has been a main hub since the birth of modern humans.
The first version at the top made 1583 and below how it looks today.
The sword held over the lion's head represents the West whereas the one below the lion represents islam (via Khazars, Bolgars, Ottomans etc. - see text below).
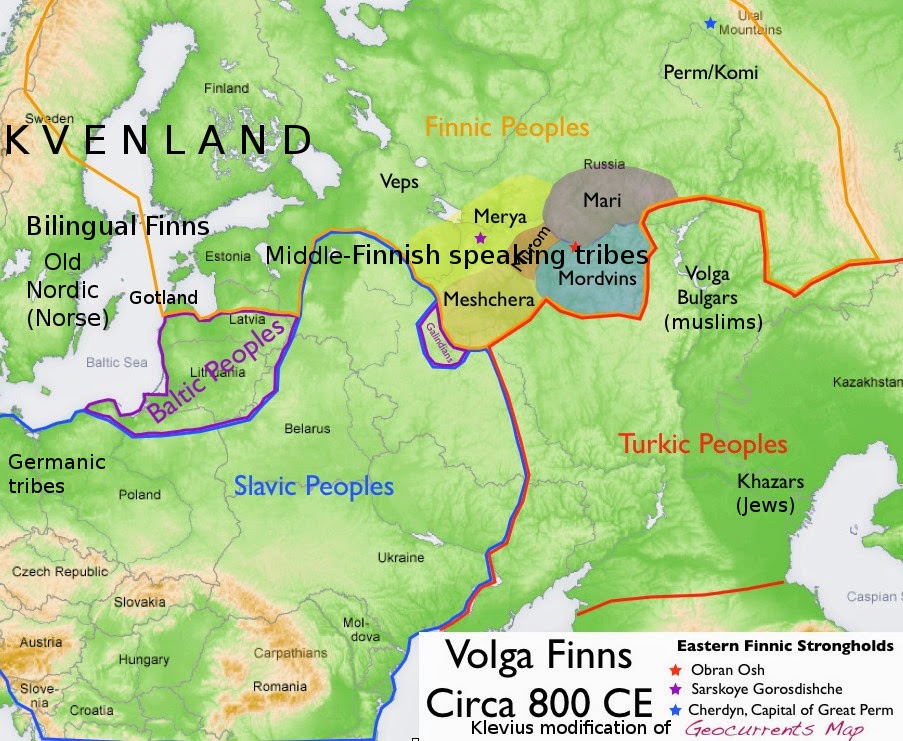
Finland/Kvenland - the home of Kalevala and the Vikings
Background
Precisely because the farming old Swedes were more numerous and wealthier than the Finnish speaking nomads, the original Finland-Swedish Vikings became "Swedisized". As a consequence the later Viking age looked more "Swedish". The oxymoron "Norwegian Vikings", however, has no place at all in history because neither Norwegian language nor Norwegians existed at that time.
Unlike muslims who only copied/stole (incl. "converts") what others had made possible, the Vikings really contributed something new.
Finland has two official languages, Swedish and Finnish. Finland is also one of the most secularized countries in the world. Finland (and huge parts of what is now Sweden and Norway) was Kvenland before the Christian crusades after which it became connected as part of Sweden for some 600 years until the 1808-9 war against Russia after which Finland became an autonomous Grand Duchy in the Russian Empire until Finland's independence 6, December 1917.
After the 1808-9 war the Swedish speaking intellectuals started a campaign, "we are no Swedes anymore, and we don't wanna be Russians - so let's be Finns". This strive made many a Finland-Swede translate their name into Finnish. It also resulted in the collection of the Kalevala epos (which Tolkien used as a basis for his stories). However, Elias Lönnroth's Kalevala was heavily influenced by a monotheist understanding. Luckily Juha Pentikäinen and others have now initiated a rewriting of the text clean from Christian monotheist influences.
Due to its location Finnish (and Saami) possesses extremely old words still in use (see below). And due to the interaction between old Nordic and Finnish a pattern emerged that can still be seen stretching from Finland all the way to Iceland (see below).
No one knows the true origin of the name Kvenland. However, Klevius qualified guess is based on its history of Nordic (and Finnish) speaking (agrarian) coastal Finns robbing beautiful girls with mongoloid characteristics (which pattern you can also trace in reading Kalevala) from its Saami and Finnish speaking neighbors. Raids with light boats was a Finnish specialty inherited from the Finnish and Russian water ways they still frequented (see Origin of Vikings). And when they heard (from the Volga Bolgars and the Jewish Khazars etc) about the enormous demand and price the muslim caliphate paid for these kind of girls the commerce quickly changed from furs to walking girls.
Due to the mix of old Nordic speaking males and Finnish speaking women an early bilingual traditon was born, which helped dealing with both Swedes and Finnish speaking "Russians". At the beginning of the Viking age the "Russians" spoke Finnish which was the main language in what is now northern and mid Russia. This also explains how Fornjotur could be the King of both Finland and Gotland as well as how Rus could become so friendly with the pre-Russians that they asked him for protection against other Vikings, Jews (Khazars) etc.
Finland has for long suffered from what Klevius calls a mongoloid complex (2003). In 1952, only seven years after the end of Finland's disastrous connection with Germany in the World War 2, apart from having its first Olympics the nation celebrated the 17-year old Armi Kuusela's victory in the Miss Universe "beauty" contest, thus finally releasing the Finns from what was considered a traumatic connection with the East and its Russian/mongoloid inhabitants.
Klevius' ethnicity
The tiny (some 300,000) Finland-Swedish ethnic minority has, apart from the tiresome, bragging and annoying islamophobe named Klevius, produced such names as Edith Södergran (modernist poet), Westermarck (anthropology), Jean Sibelius (music), Georg Henrik von Wright (Wittgenstein's successor), Lasse Wiren (athletics - double-double Olympic winner on 5,000m and 10,000m), Lindberg (music - Kraft etc), Linus Thorvald (Linux), etc etc.
This list clearly implies a Finland-Swedish complex or something (see Inside Klevius mind).
Why surprised about the fact that English is a Nordic language? Klevius has informed about it for almost a decade on the web!
* When Klevius shakes hand with native English speakers he loves to point out that 'finger', 'hand', and 'arm' all are Swedish words with exactly the same spelling and not too different pronunciation. This usually produces a nice "really". However, when he also points out that most of the non-Latin words in English also are Swedish a brief uncertain and incredulous retreat from the topic is noticeable. And, now finally the self-evident fact that even grammar is equal has been pointed out even by others.
English is a Scandinavian/Nordic (Fennoscandian*) language
* No one knows for how long Old Swedish/Nordic language(s) has been spoken in Finland. This is why not only the Scandinavian part but the whole Fennoscandian peninsula ought to be included.
Jan Terje Faarlund, professor of linguistics at the University of Oslo. "Obviously there are many English words that resemble ours. But there is something more: its fundamental structure is strikingly similar to Norwegian.
Klevius (who understands all Nordic languages incl. Finnish and most dialects): Norwegian language emerged after the Viking period (see Origin of Vikings). Its predecessor, i.e. what is called "Old Norse" but perhaps rather should be called Old Swedish or Old Nordic, is rooted in Kvenland from the cross pollination of Finnish and Nordic Germanic. Kvenish today is still very close to Finnish (more so than e.g. Estonian) yet it also contains such pecularities as meiðän ('our') which is simply meidän in Standard Finnish with a normally sounding d instead of the English sounding ð.
Kvenland (Womanland) from Finno-Ugric/Uralic to Old Swedish/Scandinavian/Nordic*
*aka "Old Norse" which might lead associations to Norway although there were no Norwegian speakers around long after the Viking age (see Origin of Vikings).
Kvenland, aka Cwenland, Kænland, Queenland, Kvinnoland, Womanland etc, is an ancient name for an area in Fennoscandia. Compare Swedish 'Kvinna' (woman) and English 'Queen' as well as Norwegian 'kone' (woman) Swedish 'kön' (sex) and English 'kin' (yes, we have Indoeuropean 'gen' but so what, where did 'gen' emerge?).
There exists a persistent "wikimyth" that Finnish language in Sweden and Norway are just a few hundred years old when in fact it's thousands of years old but due to national romanticism was explained away as caused by late immigration only.
As I already said, no one knows for sure why it was called Kvenland. However, a strong hypothesis is that the name reflects sex-slave hunt for beautiful white girls/women who were most valued on the muslim slave markets by the islamic mosques. So the Finnish empire may have existed long before it was called Kvenland.The name was just applied from the outside as a marker of its notorious records.
Kvenland appears in written sourdes from the 9th century, and from Icelandic sources written in the 12th and 13th centuries. Since the 17th century most historians have located Kvenland somewhere around or near the Bothnian Bay, in the present-day regions of Swedish Norrbotten and Finnish Ostrobothnia as well as part of Norway where there are still a Kvenish population. The traditional East Finnish name of this area was Kainuu, and it has been suggested that the Scandinavian name of Kvenland and Kainuu share etymological roots.
Around 890 CE a Northman named Ohthere visited King Alfred of Wessex who had his stories written down by Orosius.
According to Ohthere, the Norðmanna land was very long and very narrow ... and to the east are wild mountains, parallel to the cultivated land. Finnas inhabit these mountains ... Then along this land southwards, on the other side of the mountain, is Sweden ... and along that land northwards, Kvenland (Cwenaland). The Kvens (Cwenas) sometimes make depredations on the Northmen over the mountain, and sometimes the Northmen on them.
There are large [freshwater] meres amongst the mountains,[2] and the Kvens carry their ships over land into the meres, and thence make depredations on the Northmen; they have small and very light ships.
Fornjotur* (ca 160-250 CE), the Finnish King of Kvenland and Gotland, and ancestor of the Swedish Ynglinga tree and William I of England
* there is much reason to believe that the legend about Fornjotur has more truth underneath than for example the myth about Mohammed (who was allegedly born 400 years later). Hugh Kennedy (professor of Arabic language and Arabic history): "Before Abd al-Malik (caliph 685-705) Mohammed (dead 632) is never mentioned on any official document whatsoever..."Fornjotur, Fornjót, Fornjótr) was a king of Finland. His children are Ægir (the ruler of the sea), Logi (fire giant) and Kári (god of wind).
The name has often been interpreted as forn-jótr "ancient giant", and sometimes identified with the primeval giant Ymir. But it is also possible, as was suggested by Müller (1818), that it is one of a well-established group of names or titles of gods in -njótr "user, owner, possessor", which would make Fornjótr the "original owner".
How did primary stress on first syllable come from Kvenland to Iceland?
There was of course another language, Kvenish-Finnish, that was present in Fennoscandia and somehow influenced the ancient Norse language.
Finnish possesses some of the oldest words in the world, some of them still in their original Uralic form. In fact, the old Finnish stem seems to be closer to its distant roots than other Finno-Ugric languages despite the fact that Finland has been the most modernized of them all.
Klevius linguistic question: How was the strange affinity between Indoeuropean Icelandic and Uralic Finnish created between Kvenland and Iceland?
Whereas Indoeuropean languages are strongly rooted in a Neolithic agricultural past Uralic languages are rooted in hunting/gathering societies i.e. pre-Neolithic.
Indoeuropean Old Norse developed into "Western" and "Eastern" variants. Western Norse covered Norway and overseas settlements in Iceland, Greenland, the Faroe Islands and the Shetland Islands, while Eastern Norse developed in Denmark and south-central Sweden and coastal Finland.
The language of Iceland and the non Finnish or Saami Fennoscandia was practically the same up until the 14th century, when they started to deviate from each other.
During the late Old Norse period and this period there was also a considerable adoption of Middle Low German vocabulary. Similar development in grammar and phonology happened in Swedish and Danish, keeping the dialect continuum in continental Scandinavia intact, but with greater dialectal variation. This process did not, however, occur in the same way in Faroese and Icelandic. These languages remain conservative to this day, when it comes to grammar and vocabulary, so mutual intelligibility with continental Scandinavia was lost.
The Uralic languages belong to a single Eurasian belt of agglutinative languages together with the Altaic languages streching from Fennoscandia in the west to Japan in the east
Not only typological parallelism, but also stress on the first syllable as well as lack of third person pronoun sex segregation (e.g. Finnish 'hän' instead of 'he/she' apartheid) is accompanied by areal adjacency, allowing us to speak of a distinct Ural-Altaic language area and language type we may call Eurasiatic.
Some roots for Eurasiatic: mi (what?, mi/kä or mi/tä in modern Finnish), pälä (two), akʷā (water), tik (one or finger), konV (arm 1), bhāghu(s) (arm 2), bük(ä) (bend or knee), punče (hair), p'ut'V (vagina or vulva), snā (smell or nose), kamu (seize or squeeze), and parV (the verb to fly)
Modern Finnish preserves old words equal or almost equal more often than other languages
Examples of reconstructed Proto-Uralic words:
Body parts and bodily functions: *ïpti hair on the head, *ojwa head, *śilmä eye (same as in modern Finnish), *poski cheek (same as in modern Finnish), *kä(x)li tongue ('kieli' in modern Finnish), *elä- to live ('elää' in modern Finnish), *ka(x)li- to die ('kuolla', and 'kuoli' in imperf), *wajŋi breath (in Finnish 'vainaja' means a dead), *kosi cough, *kunśi urine ('kusi' in modern Finnish), *küńili tear ('kyynele' in modern Finnish), *se(x)ji pus.
Kinship terms: *emä mother (same in modern Finnish), *čečä uncle ('setä' in modern Finnish), *koska aunt, *mińä daughter-in-law ('miniä' in modern Finnish), *wäŋiw son-in-law ('vävy' in modern Finnish).
Verbs for universally known actions: *meni- to go ('mennä', 'meni' in imperf in modern Finnish), *toli- to come ('tulla', 'tuli' in imperf in modern Finnish), *aśkili- to step ('askel' is step in modern Finnish), *imi- to suck ('imi' is sucked in modern Finnish), *soski- to chew, *pala- to eat up ('pala' is a piece in modern Finnish), *uji- to swim ('ui' is swim in imperf in modern Finnish), *sala- to steal ('salata' means to hide in modern Finnish), *kupsa- to extinguish ('kupsata' used for to die in modern Finnish).
Basic objects and concepts of the natural world: *juka river ('joki' in modern Finnish), *toxi lake, *weti water ('vesi/vettä' in modern Finnish), *päjwä sun (same but also day in modern Finnish), warmth, *suŋi summer ('suvi' in modern Finnish), *śala- lightning ('salama' in modern Finnish), *wanča root ('vanka', 'vankka' means steady in modern Finnish), *ko(x)ji birch, *ka(x)si spruce ('kuusi' in modern Finnish), *sïksi Siberian pine, *δ'ï(x)mi bird cherry
Elementary technology: *tuli fire (same in modern Finnish), *śüδi coal, *äjmä needle, *pura drill ('pora' in modern Finnish), *jïŋsi bow ('jousi' in modern Finnish), *jänti bow string, *ńï(x)li arrow ('nuoli' in modern Finnish), *δ'ümä glue ('liima' in modern Finnish), *lïpśi cradle, *piksi rope, *suksi ski (same in modern Finnish), *woča fence.
Basic spatial concepts: *ïla below ('alla' in modern Finnish), *üli above ('yli' in modern Finnish), *wasa left ('vasen' in modern Finnish), *pälä side.
Pronouns: *mun I (meaning mine in modern Finnish), *tun you ('sun' meaning yours in modern Finnish), *ke- who (same in modern Finnish), *mi- what (same in modern Finnish).
The reconstructed vocabulary is compatible with a Mesolithic culture (bow, arrow, needle, sinew, but also rope, fence, cradle, ski), a north Eurasian landscape (spruce, birch, Siberian pine), and contains interesting hints on kinship structure.
The Vikings were bilingual (Finland-Swedes) Goths who could communicate both with the Finnish tribes as well as with the old Nordic/German people
In the Viking world the Jewish slave empire (Chazaria) played an important role in establishing the slave raid and trade system that served the enormous islamic hunger for white sex slaves.
Karelia's old coat of arms.
Karelia bordered the medieval Novgorod republic which was ransacked by muslim Bolgars who hunted for slaves. The southern part became an important hub in the islamic slave finance as Vikings and Kazar Jews etc served the islaic caliphate in the south and later on the Ottoman Turks.
Fair skinned female sex slaves from northern Europe were the by far most valuable according to islamic price lists
(see more about this here)Most of what you read about Vikings on the web is wrong. The Viking age started already before 750 in the east (because of islamic demand for sex slaves). So forget about Britain 786. Also remember that if you see the words Norway or Norwegians mentioned re. Vikings then throw the link/book away. There was no Norway or Norwegians or a Norwegian language during the Viking age! Educate yourself on Origin of the Vikings.
In 882, Rurik's successor, Oleg of Novgorod, conquered Kiev and founded the state of Kievan Rus.
After the Kievan Russian state began to disintegrate in 1132, slaves became much more numerous as inhabitants of neighboring East Slavic principalities (much of the territory between Poland-Lithuania and the Volga River) became fair game for enslavement.
Jewish merchants took East Slavic slaves from Novgorod to western destinations. Other East Slavic slaves were continuously "harvested" by the Turkic peoples (Tatars) inhabiting the southern and eastern frontiers of Rus' and subsequently sold to buyers mainly in the Arab countries.
The Mongol invasions into Rus' from 1236-1240 accelerated the disintegration of Kievan Rus' that had commenced in 1132.
Continuous Tatar slave raids replaced those of the pre-1240 Turkic peoples who had roamed the Ukranian steppe. In these centuries the word "slave" was borrowed from the ethnonym "Slav."
During the ensuing period of the "Tatar yoke" (1237-1480), the export of slaves through Novgorod continued and the Novgorodian slave market at the intersection of Slave and High Streets was the most active business locale in the entire Republic of Novgorod, which encompassed much of Russia north of the Volga to the White Sea.
The Crimean Tatars had converted to islam in the 1300s and in 1475 the Crimean Khanate became a protectorate of the Ottoman Empire while itself still clinging to power over the Duchy of Muscovy. In 1480, the Muscovites threw off the "Tatar Yoke" and began the unification of Russia under Slavic rulers. By 1503, those rulers would declare Russia the Third Roman Empire, and take the title of Tsar.
The Crimean Tatars made use of their strategic position between the Ottomans and the Russians and supplied slaves for the Ottoman Janissary corps from the neighboring peoples to an enormous extent yet to be fully mapped.
Greedy rulers either married a muslim and naively agreed* to convert or just found islam the perfect sword for evil but profitable slave finance
* Islam is an evil dead end. A totalitarian harpoon that has only one direction unless it's stopped. This is one of the many reasons why islam is completely out of sync with Human Rights - a fact that not only Klevius but also OIC has realized!
Little is known about the timeline of the islamization of Inner Asia and the Turkic peoples who lay beyond the bounds of the caliphate. Around 7th century and 8th century, there were some states of Turkic peoples like Turkic Khazar Khaganate and Turkic Turgesh Khaganete who fought against the caliphate in order to stop Arabization and islamization in Asia. From the 9th century onwards, the Turks (at least individually, if not yet through adoption by their states) began to convert to islam. The Bulgars of the Volga, to whom the modern Volga Tatars trace their islamic roots, are noted to have adopted islamic evil early on. When the Friar William of Rubruck visited the encampment of Batu Khan of the Golden Horde, who had recently completed the Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria, he noted "I wonder what devil carried the law of Machomet there".
Different political functions of the islamic myth to legitimate power
Quite contrary to the populist academic discourse that within an islamic worldview, the production of "eventually" correct ritual behavior can be a gateway for "the grace of Allah" to produce "correct belief", the crude reality of islam's own tenets points clearly - and without the slightest anomaly from non-islamic history in sight - to a profitable parasitic formula crudely chiseled on pre-existing Judaic dogmas. This formula, which in one sweep eliminates otherwise "puzzling" historical events, goes like this (taken from www.klevius.info):
The root formula of Islam (Klevius 2001)
Slavery+"infidel" racism+sex segregated rapetivism+anti human rights Sharia/apostasy ban.
Why isn't the worst crime ever against humanity criminalized, but instead protected by the very Human Rights islam opposes?!
Converts to islam don't have to understand anything to be a "good muslim" simply because accepting totalitarian islam is the only proof needed. However, other muslims might not approve of it...


















































































































































































No comments:
Post a Comment